Bitcoin, kao najpopularnija i međunarodno najpriznatija kripto valuta, ima unapred određeni volumen koji je limitiran na 21 milion čija će se „emisija“ završiti do 2140. godine. Dok je ponuda ovako kontrolisana, tražnja zavisi od stepena prihvaćenosti od strane tržišta.
Kada vam neko pomene blockchain prva asocijacija neminovno je Bitcoin. Tehnologija originalno jeste razvijena kao deo ove kripto valute, ali je ipak daleko više od toga. Bilo da je reč o identifikaciji, ili nekom vidu transakcije blockchain je početak velikih promena u načinu na koji svi zajedno poslujemo.
Pre nego što zaronim dublje u temu, osvrnuo bih se na jednu situaciju iz istorije. Naime, vizantijski generali opkolili su neprijateljski grad. Svaki od generala nalazio se sa svojom vojskom negde oko grada i generali su geografski bili razdvojeni. Komunikacija među generalima je išla preko kurira, koji prenose poruke. Da bi napad uspeo, generali su morali da se dogovore oko zajedničkog nastupa – da krenu svi odjednom u dogovoreno vreme. Međutim, problem je bio taj što među generalima, pa i među kuririma mogu da postoje izdajnici – ljudi koji rade za neprijatelja i koji će namerno preneti pogrešnu poruku kako bi sabotirali napad. Kako organizovati prenošenje poruka među generalima tako da akcija uspe, bez obzira na izdajnike?
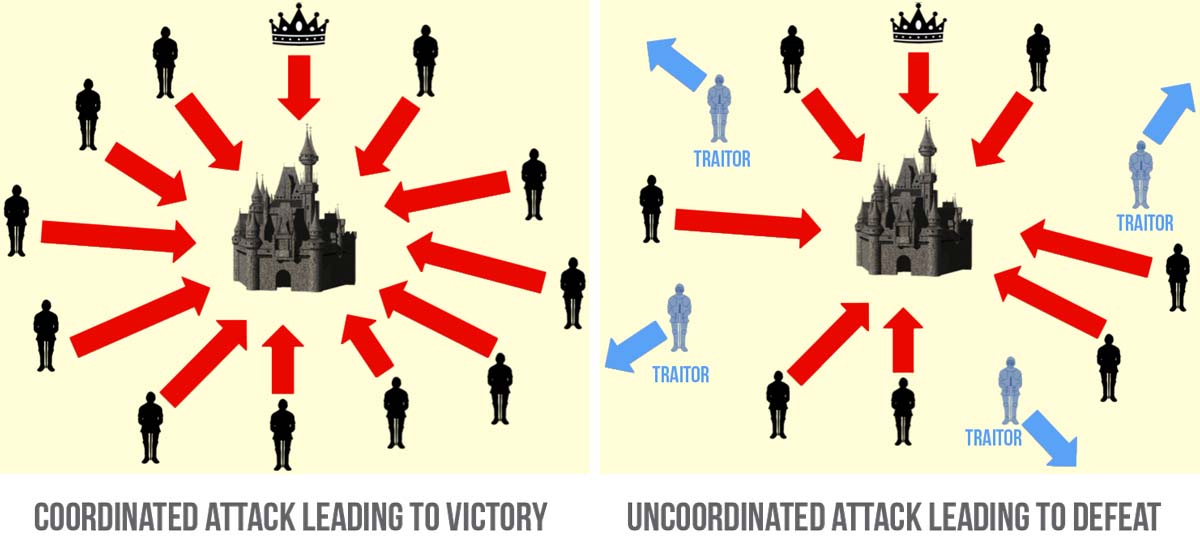
Rešenje ovog problema postoji i u pitanju je veoma kompleksan matematički algoritam koji se razvio početkom 21. veka. Pojavom bržih kompjutera, ovaj problem postao je rešiv za kraće vreme. U praksi, ovo je značilo da smo dobili način da se uspostavi potpuno poverenje između dve osobe na internetu koje se uopšte ne poznaju. To je otvorilo čitav novi spektar mogućnosti – a jedna od tih mogućnosti je digitalni novac.
Postoje razne teorije, neke su čak i teorije zavere, o tome ko je kreirao Bitcoin kao i to da li njegov tvorac uopšte postoji. Zvanično, sve je počelo u januaru 2009. godine kada je Satoshi Nakamoto započeo ovu kripto-revoluciju. Danas postoji preko 1300 aktivnih kripto valuta, a njihov značaj i upotreba se konstantno povećavaju. Svoj procvat doživele su najpre zbog garantovane privatnosti učesnika u transakcionom sistemu.
Dok je promet i vrednost standardnih valuta pod uticajem regulatornih tela i mera monetarne politike, kriptovalutama vrednost ne može da odredi jedan autoritet, bilo politički ili finansijski.
Bitcoin, kao najpopularnija i međunarodno najpriznatija kripto valuta, ima unapred određeni volumen koji je limitiran na 21 milion čija će se „emisija“ završiti do 2140. godine. Dok je ponuda ovako kontrolisana, tražnja zavisi od stepena prihvaćenosti od strane tržišta.
Na mala, ili malo veća vrata, Bitcoin polako počinje da ulazi u mainstream vode. Do sada je već našao svoj put do bankomata, plaćanja u sertifikovanim kompanijama, pa čak i do međubankarskog tržišta.
Brige oko mogućih zloupotreba, ali i zamerke upućene samom sistemu, ipak postoje. Osim toga, dalji razvoj mogu da ograniče i uspore i pritisci od strane konkurentskih sistema kao što su Visa i Matercard, nedostatak regulative koja sprečava velike igrače da se upuste u igru, nedostatak poverenja zbog izrazite volatilnosti, činjenica da samo 880 učesnika drži 50% ukupne vrednosti, ali i nezaobilazan strah od hakerskih napada.
Tu dolazimo do glavnog zadatka blockchaina kao tehnologije poverenja.

U osnovi svega je decentralizovan sistem bez jednog konkretnog vendora-autoriteta, koji određuje potrebnu hardversku podršku i njenu lokaciju kao što je slučaj kod tradicionalnih softverskih rešenja. Svi učesnici u sistemu sa različitih krajeva sveta doprinose svojim procesorskim moćima utvrđivanju jedinstvene istorije.
Šta je i kako zapravo funkcioniše?
Blockchain je šifrovana baza podataka deljena od strane velikog broja računara koji su deo jedne zajednice tj. sistema. Njegova sposobnost da smanji mogućnost bezbednosnih upada, čak i od vlastitih operatera, je karakteristika koja ga čini tako revolucionarnim.
Kada bi u jednoj rečenici opisali blockchain rekli bismo da je to tehnologija koja služi da prikuplja i slaže podatke u blokove, a zatim da ih bezbedno poveže u lance koristeći kriptografiju.
Prikupljanje i slaganje se ne obavlja sâmo, već to rade „rudari“ tj. kompjuteri takmičenjem u rešavanju određenog problema (proof of work). U proseku na svakih 10 minuta, pobednički miner objavljuje pregled obrađenih transakcija i slaže ih u važeći blok. Za obavljen posao biva nagrađen novim jedinicama određene kriptovalute.
Svaki završeni blok šalje se preko mreže, povezuje sa prethodnim i tako se stvara lanac tj. blockchain.
Ako ste pomislili da je ovo dobar način da zaradite novac, treba da imate na umu da je rudarenje neverovatno konkurentno, rizično i praćeno velikim početnim investicijama u svetu u kome se tehnologija brzo menja. Neke firme u Kini su pokušale da se obogate ovim poslom, ali je ceo sistem tako dizajniran da ni jedna velika firma ne može samo kupovinom i angažovanjem velikog broja moćnih grafičkih karti da zagarantuje i veliku finansijsku dobit.
Suštinski, blockchain predstavlja evidenciju transakcija u vidu glavne knjige. Jednom upisana transakcija, sačuvana je zauvek. Sâm pojam transakcija treba shvatiti široko. To može biti svako kretanje novca, robe ili obezbeđenih podataka. Blockchain je dizajniran tako da čuva informacije na način koji onemogućava dodavanje, uklanjanje ili promenu podataka bez da to ne vide drugi učesnici.
Ključ za sigurnost bloka i cele ove priče leži u nečemu što se zove hash funkcija,koja upotrebom kriptografske matematike preuzima informacije iz svakog bloka i kreira jedinstveni niz znakova tj. hash.
Hash iz jednog bloka se dodaje podacima u sledećem bloku što veze između blokova čini praktično neraskidivim. Pri svakom kreiranju novog bloka, njegov hash biva umotan u sledeći i tako kroz čitav lanac.
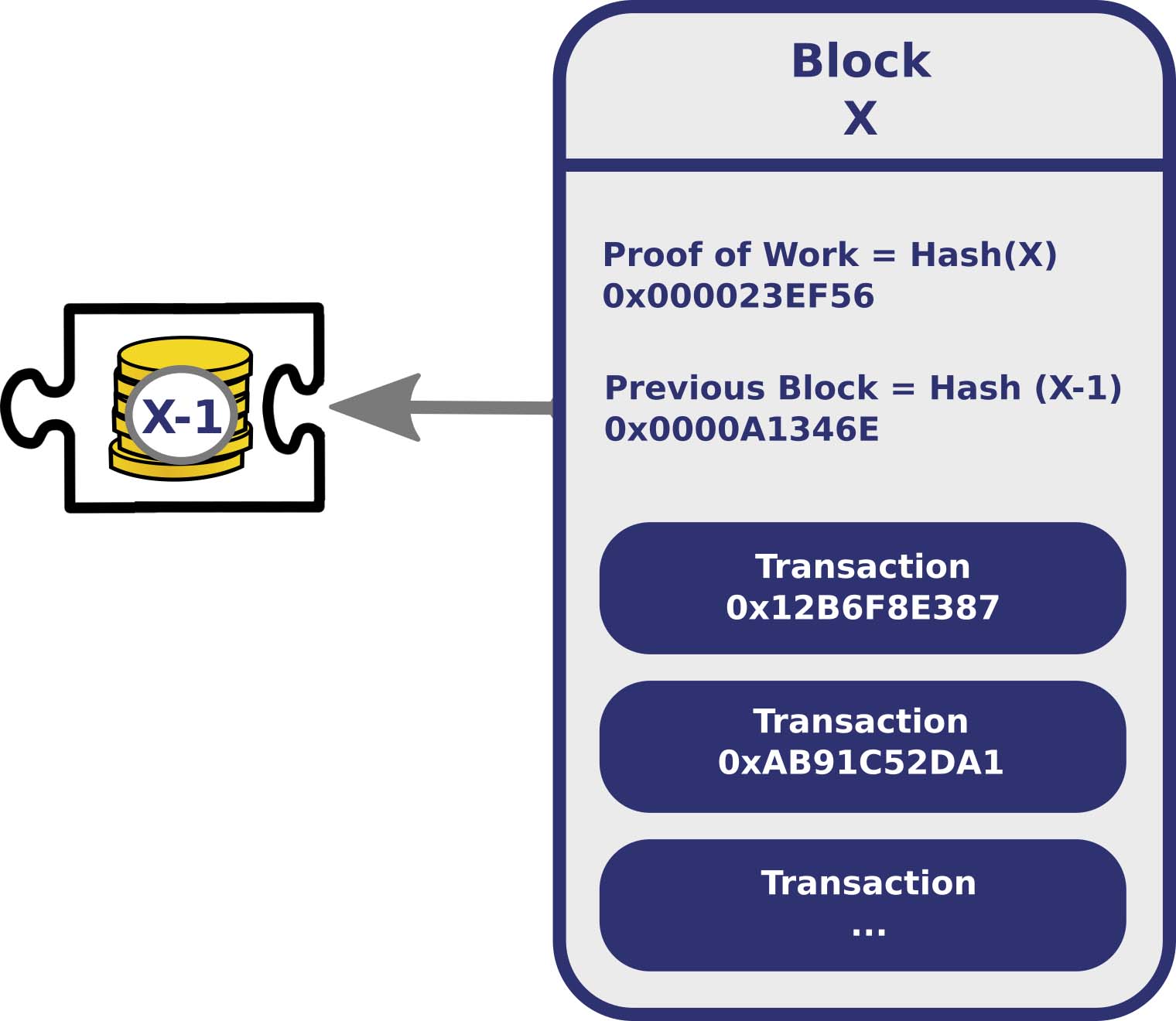
Ovaj postupak je upravo ono što onemogućava bilo kakav pokušaj izmene prethodno kreiranog bloka. Čak i ako bi neki hrabar i uporan haker pokušao i uspeo da promeni bar jedno slovo, blok ne bi mogao da bude prebačen u sistem glavne knjige pošto se hash koji je kodiran u sledećem bloku više neće podudarati. I tu padaju u vodu svi napori nesrećnog hakera.
Potencijal blokchaina ogleda se u širokom spektru mogućih primena. Nova tehnologija će redefinisati način na koji obavljamo transakcije bez obzira nešto kupujemo, prodajemo, izvršavamo obaveze prema državi, sklapamo ugovore ili nam je potrebno da proverimo autentičnost nečega. Brži i sigurniji način provere informacija koje su od ključnog značaja za to što radimo je omogućeno kombinacijom otvorenosti interneta sa sigurnošću kriptografije.
Da bih vam malo dočarao kako ovo u praksi može da izgleda uzmimo jedan jednostavan primer.
Recimo da želite da kupite karte za omiljeni koncert, ali niste baš sigurni da ćete preko postojeće online platforme dobiti ispravnu željenu kartu. Tu nastupa blockchain koji ide direktno do izvora, zaobilazi agente i treća lica i osigurava da je karta koju su kupili pouzdana i originalna.
Kada se karta proda, dodeljuje joj se adresa tj. niz podataka koji se javno mogu videti na blockchainu. Vaš identitet kao kupca se nigde ne vidi, ali ćete samo vi dobiti privatni ključ koji je jedini alat za „otključavanje“ adrese i preuzimanja karte.
Ova tehnologija takođe može da omogući efikasnija tržišta i uklanjanje uskih grla. Na finansijskim tržištima recimo, trgovina se obavlja u par sekundi, ali razmena imovine i plaćanja može da potraje par dana i uključi veći broj učesnika. Sve to može dovesti do grešaka, kašnjenja, dodatih troškova i nepotrebnih rizika. Blockchain omogućava direktan kontakt i završetak transakcije za osam do deset minuta.
Sklapanje pametnih ugovora (smart contact) takođe je novina koja je deo ove revolucije. Ugovor je sada deo računarskog koda koji opisuje transakciju korak po korak, može povezati više blokova informacija i razmeniti sredstva po potrebi, u cilju da se transakcija ili njen deo izvrši.
Još jedna važna primena je čuvanje i upotreba osetljivih informacija. Lična dokumenta se tradicionalno izdaju i kontrolišu od strane državnih organa. Digitalno izdata identifikacija putem blockchaina može biti sigurniji i brži mehanizam. Međunarodni i samo vaš blockchain, dostupan bilo gde u svetu, omogućio bi vam da dokažete svoj identitet, da se povežete sa članovima porodice i da primate novac bez bankovnog računa gde god da se nalazite.
Gde se nalazimo danas?
Neke kompanije su u pilot fazi projekata sa blockchain tehnologijom. Rani prihvatioci su takođe aktivni. Sledeća očekivana faza je i da oni oprezniji krenu da bi ih zatim ispratili svi ostali.
Iako je potencijal za upotrebu veliki, tehnologija je još uvek u početnim fazama. Pre nego što se naširoko usvoji moraju se prevazići neke prepreke.
Čak i najbolje razvijena blockchain tehnologija koja stoji iza Bitcoina, može da obradi pet do osam transakcija u sekundi. To je i dalje neuporedivo sa procesorima transakcija kao što su Visa i MasterCard koji mogu da obrade 10 000 puta više transkacija u istoj toj sekundi.
Rešenje nije tu iza ćoška, ali jeste na vidiku. Celom procesu, kao i obično, mnogo će pomoći pioniri koji su spremni da ulože vreme i resurse kako bi se upotreba kriptografske matematike i napretak tehnologije realizovao kroz opštu prihvaćenost blockchain tehnologije. Jedno je sigurno. Njeno vreme tek dolazi.



